When deploying a VM running certain operating systems such as Windows Server, a license is added to the boot disk of that instance. This license is used for billing PAYG licensing.
While the cost for a Windows Server license is the same irrespective of the version, you may be inclined to want to update the associated license in order to reflect the correct version being billed.
Through recent upgrades, licenses are now mutable (within limits). This allows to upgrade licenses and ensure that the right version of the license is assigned to a particular VM.
Scenario#
Imagine that you have a VM that is running Windows Server 2022 and you are upgrading to Windows Server 2025. You want the GCE license to reflect the same. There are a few steps that you need to go through.
Assigning a new license#
The new license can either be appended or the existing license can be replaced.
Appending the license#
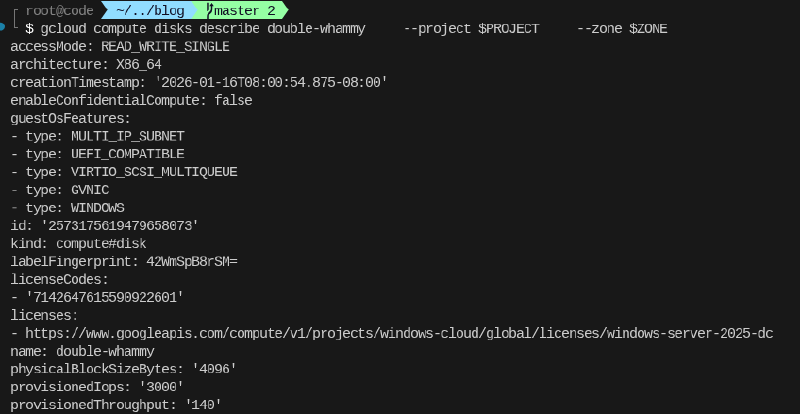
The following snippet will append the Windows Server 2025 license to an existing disk double-whammy:
DISK=double-whammy
ZONE=europe-west4-a
gcloud compute disks update $DISK \
--zone $ZONE \
--append-licenses https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/windows-cloud/global/licenses/windows-server-2022-dcThis is what the disk looks like now:
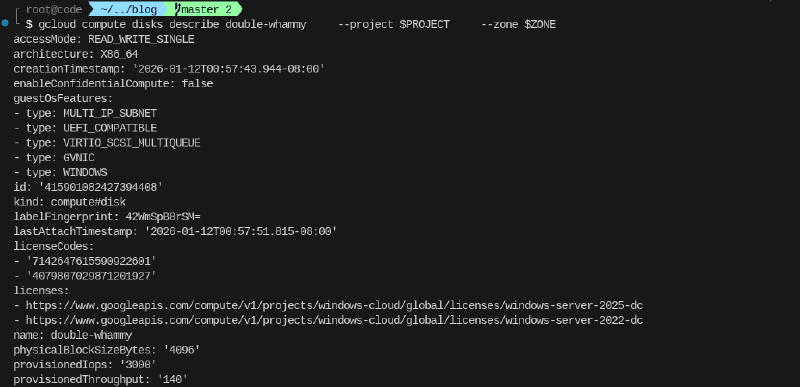
When appending the license it is important to remove the old licese. As noted above if that is not done, all licenses will be charged leading to unecessary cost.
Removing the old license#
The following command will remove the old license.
DISK=double-whammy
ZONE=europe-west4-a
gcloud compute disks update $DISK \
--zone $ZONE \
--remove-licenses https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/windows-cloud/global/licenses/windows-server-2022-dcReplacing the licese#
Instead of appending the new and removing the old license. The license can also be straight up replaced in a single operation.
DISK=double-whammy
ZONE=europe-west4-a
gcloud compute disks update $DISK \
--zone $ZONE \
--replace-license https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/windows-cloud/global/licenses/windows-server-2022-dc,https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/windows-cloud/global/licenses/windows-server-2025-dcThis will update the license with the new one in a single operation: