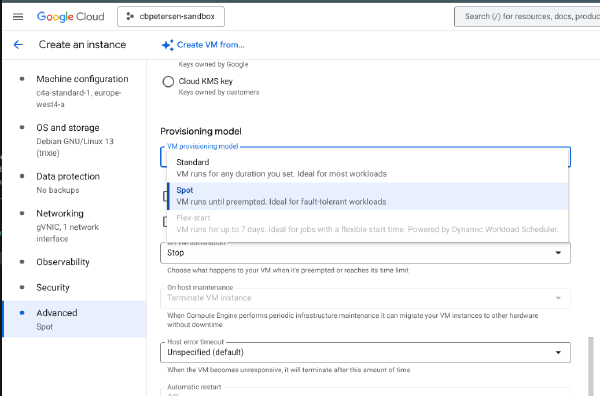
In a previous article I have explained how to change the provisioning of a VM from being preemtible to Standard. There are situations where you have a VM deployed with the Standard provisioning model but you want to reduce its cost and the workload is stateless or interruptible.
All good examples on why you may want to switch the provisioning model from Standard to Stot. Here is how you do it using gcloud:
Changing the provisioning model using gcloud#
Before you can change the provisioning model, you need to shut down the VM.
gcloud compute instances set-scheduling spotty \
--provisioning-model SPOT \
--maintenance-policy TERMINATE \
--preemptible \
--no-restart-on-failureThat’s it. Just like that your VM is now running as a Spot VM. Be aware that it can be preempted at any time so make sure your workload supports that.